Hey everyone! To our Advantech partners and friends curious about our technology, hello!
As a company constantly pursuing technological breakthroughs, we are always working behind the scenes, exploring new technologies that can make our products more powerful and convenient. Today, we want to share an interesting experimental process with you, featuring something you might have heard of but aren’t quite familiar with: “ADB OTA”!
You might be thinking, OTA? Isn’t that for updating software on phones? Exactly! OTA (Over-The-Air) technology allows devices to receive and install updates over the network, without needing cables or on-site visits. Isn’t that super convenient? This technology is already widespread in the consumer electronics field, but its application potential is even greater on our industrial and commercial-grade devices! Imagine digital signage, industrial controllers, or smart retail equipment deployed worldwide – if they could all be easily updated remotely, think of the labor and time costs saved!
And what about ADB (Android Debug Bridge)? Simply put, it’s a tool commonly used by Android developers that allows a computer to communicate directly with an Android device and execute various commands, acting like an engineer’s “secret passage.” This time, our engineering team had a sudden idea: could we use this “secret passage” to test and verify the OTA update process? This would not only provide a flexible testing method but might also be useful in certain specific development or maintenance scenarios in the future!
Therefore, the objective of this experiment was clear: to verify whether OTA updates can be successfully performed on our devices using ADB commands.
Experiment Revealed: How to Play with ADB OTA? #
Next, let’s take a look at how the engineers conducted this experiment! The whole process is like performing “remote surgery” on the device, but don’t worry, we’ll explain it in the simplest terms.
First, we need to prepare the “new system” files to be updated, which is the OTA update package. This package contains all the necessary data for the system update.
- Operating System Image Version:

- OTA Version:

After preparing the update package, the next step is to connect to the device via ADB and execute the update commands.
ADB Connection and Update Steps (Engineer’s Perspective, Plain Language Explanation) #
-
Find the device’s “House Number” (IP Address): Just like needing an address to send a letter, the computer needs to know the device’s IP address to connect to it. We can easily find this through the device’s settings software.
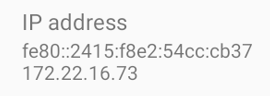
-
Establish ADB Connection: Open a command prompt or terminal on your computer (host) and enter the command to tell the computer which IP address device to connect to.
$ adb connect 172.22.16.73:5555 -
Obtain the device’s “Highest Authority” (root privileges): To place the update files in the device’s system directory, we need to obtain root privileges, which is like “administrator privileges” on a computer. Note that this step needs to be re-executed every time the device restarts.
$ adb root -
Reconnect (if step 3 was executed): After obtaining root privileges, the ADB connection might be interrupted and needs to be reconnected.
$ adb connect 172.22.16.73:5555 -
Decompress the update package and transfer files: The OTA update package is usually in zip format, containing the main update data file
payload.binand a description filepayload_properties.txt. We need to decompress these two files and then transfer them to the specified directory on the device via ADB.
The commands for transferring files are as follows:
$ adb push payload_properties.txt /data/ $ adb push payload.bin /sdcard/The entire process of connecting and transferring files looks like this in the command line:
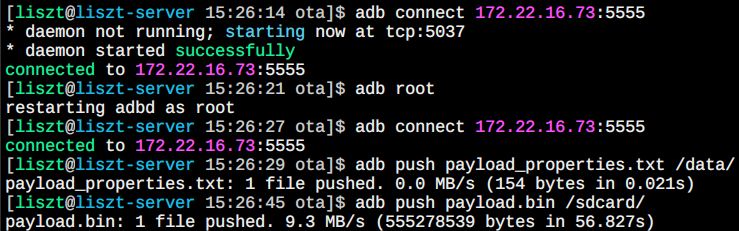
-
Enter the device’s “Internal System” (adb shell): Now that the files have been transferred to the device, we need to “log in” to the device’s system environment to execute the update commands.
$ adb shell -
Execute the OTA update command: In the device’s system environment, we use the
update_engine_clienttool to initiate the update process. The command tells the tool where to find the update file (payload.bin) and the relevant update information (payload_properties.txt).rsb3720_a1:/ # export payload=$(cat /data/payload_properties.txt) rsb3720_a1:/ # update_engine_client --payload=file:///sdcard/payload.bin --update --headers="$payload" -
Monitor the update process (logcat): After the update command is executed, the device will start the update. We can use the
logcatcommand to view the system logs, monitor the update progress, and check for any errors.rsb3720_a1:/ # logcatThe logs will continuously scroll, showing what the system is doing. Among these dense logs, we need to look for messages related to
update_engine. These messages will tell us which stage the update is at, for example:overall progress 10%,overall progress 20%… show the update progress.ActionProcessor: finished DownloadAction with code ErrorCode::kSuccessindicates successful download/application of the update file.ActionProcessor: finished FilesystemVerifierAction with code ErrorCode::kSuccessindicates successful file verification.Update successfully applied, waiting to reboot.indicates that the update has been successfully applied, waiting to reboot.
Log snippet example:
... (前面是更新過程的日誌) 09-13 07:33:07.344 527 527 I update_engine: [0913/073307.344502:INFO:delta_performer.cc(208)] Completed 895/895 operations (100%), 555278539/555278539 bytes downloaded (100%), overall progress 100% ... (中間是驗證檔案的日誌) 09-13 07:33:22.947 527 527 I update_engine: [0913/073322.947822:INFO:update_attempter_android.cc(454)] Processing Done. 09-13 07:33:22.951 527 527 I update_engine: [0913/073322.951487:INFO:update_attempter_android.cc(462)] Update successfully applied, waiting to reboot. ... (後面是清理和記錄日誌) 09-13 07:33:24.039 527 527 I update_engine: [0913/073324.039591:INFO:metrics_reporter_android.cc(29)] uploading 0 to histogram for metric ota_update_engine_successful_update_reboot_count ...When you see phrases like
Update successfully appliedandErrorCode::kSuccess, as well as success indicators likeota_update_engine_successful_update_reboot_count, it means the update files have been successfully written to the device! -
Restart the device: After the update files are written, the device needs to restart to load the new system. We enter the
rebootcommand in the ADB shell environment to restart the device.^C (按Ctrl+C退出logcat) 130|rsb3720_a1:/ # rebootAfter the device restarts, it will run the updated system version!
Experiment Results and Value #
This experiment of performing OTA updates via ADB was very successful! We verified that on Advantech devices, the ADB tool can be used to execute the complete OTA update process, from file transfer to command execution, everything went as smoothly as expected.
The success of this experiment once again demonstrates Advantech’s strong capabilities in software and hardware integration. Although ADB OTA is primarily used for development, testing, or specific maintenance scenarios, unlike traditional OTA which is directly operated by end-users, it provides a powerful and flexible tool that allows our engineers and partners to perform system debugging and verification more conveniently.
This also means:
- More efficient development and testing: Engineers can quickly push new system versions to test devices, accelerating the development cycle.
- Flexible maintenance options: In certain special circumstances where standard OTA servers cannot be used for updates, ADB OTA provides a direct alternative.
- Demonstration of technical proficiency: Successfully implementing ADB OTA proves our deep understanding and mastery of the underlying system update mechanism.
Conclusion and Future Outlook #
This ADB OTA experiment is a microcosm of Advantech’s continuous investment in R&D and active exploration of new technologies. We not only provide stable and reliable hardware platforms but are also committed to offering more diverse and convenient solutions at the software level.
In the future, we will continue to deepen our research in the field of OTA technology, exploring more automated and secure remote update methods, allowing our customers to easily manage and maintain their Advantech devices no matter where they are. We believe that through continuous innovation and experimentation, Advantech will be able to bring more intelligent and efficient solutions to various industries!
Thank you for reading. If you have any interest or questions about Advantech’s technology, please feel free to contact us!